A function that can accept any number of arguments, means number of arguments are not predefined that is a variable argument list function . In a typical function we can only pass a fix number of arguments while calling.
Above is the gcc screenshot of a fixed argument function sum(), sum is a user defined function that can accept only two arguments. If we call sum() with more than two or less then two argument then it will generate Linker error.
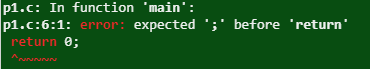
We cannot call sum as sum(a,b,c).While doing so compiler generates error as below :-
Question is can we create our own function like printf(),scanf() that have no fixed number of arg.
*Can we create our own sum() function** which can accept n number of arguments ?
We can achieve this by using Variable length argument feature.
How to do that ? :-
******************************************************************************
Variable argument length(Variable argument list) feature allows the function to receive n number of arguments in a function.
How to define a variable argument function?
There are two ways :-
- We can pass a fixed argument that argument indicates how many variable arguments are there.
- Pass a null at the end to indicate number of variable arguments.
Irrespective of the two ways.
We define a function using (...) three dots as one of the arguments to indicate its of variable argument length.
Exp:-
int sum(int,...);
int sum(char *n,..);
-First we will discuss method 1
To understand method one we can undergo linux man page of va_start
cmd$ man va_start
cmd$ man va_start
Step 1: Create a variable(pointer similar to char*) of type va_list
va_list v;
Step 2 : Call function va_start to specify total no. of arguments to fetch .
va_start(v,n);
For the above program:
va_start(v,n) n being the total no. of arguments starting from va_list v.
this value becomes va_start(v,3) for the sum(3,i,j,k) specifying to traverse from va_list v to n .
Step 3: Use va_arg to fetch the values of the type of argument passed as 2nd argument (integer in the case of the above program)
s=s+va_arg(v,int);
For the above program this function is used to fetch the value of all the variable argument ** provided the type of argument
va_arg( v , int ) Integer being the type of argument in function.
Implies function sum(3,i,j,k) > sum(3,50,60,70) the values of the variable argument list is fetched.
va_list v;
Step 2 : Call function va_start to specify total no. of arguments to fetch .
va_start(v,n);
For the above program:
va_start(v,n) n being the total no. of arguments starting from va_list v.
this value becomes va_start(v,3) for the sum(3,i,j,k) specifying to traverse from va_list v to n .
Step 3: Use va_arg to fetch the values of the type of argument passed as 2nd argument (integer in the case of the above program)
s=s+va_arg(v,int);
For the above program this function is used to fetch the value of all the variable argument ** provided the type of argument
va_arg( v , int ) Integer being the type of argument in function.
Implies function sum(3,i,j,k) > sum(3,50,60,70) the values of the variable argument list is fetched.